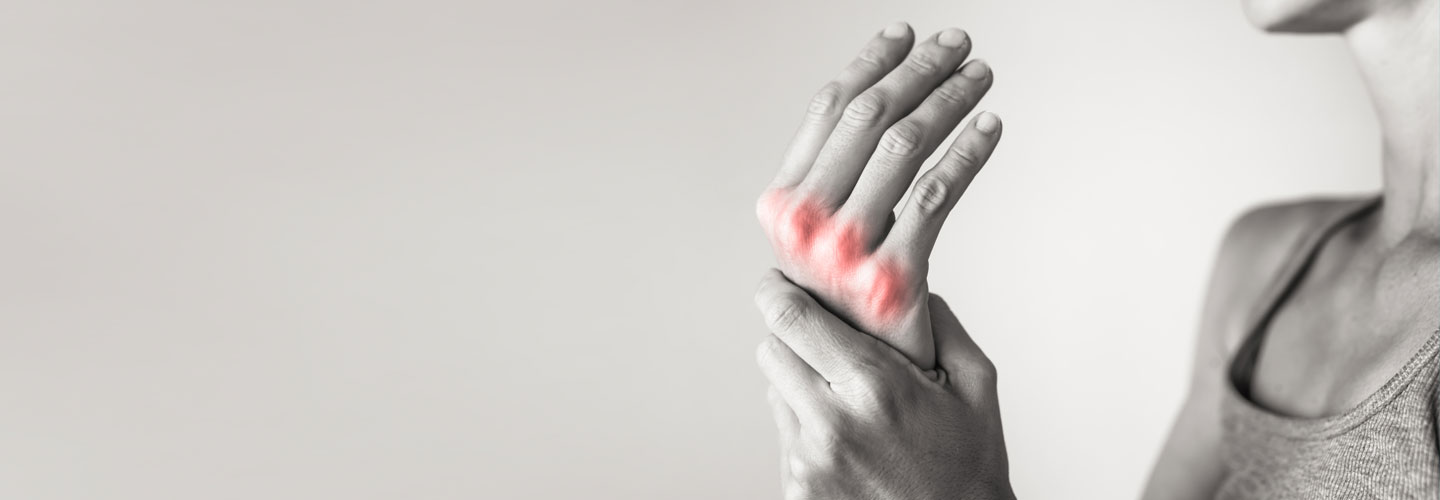
Also known as rheumatoid arthritis, it is a chronic inflammatory disorder that can affect more than just your joints. It's a type of autoimmune disorder that occurs when your immune system mistakenly attacks your own body's tissues. Unlike the wear-and-tear damage of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis affects the lining of your joints, causing a painful swelling that can eventually result in bone erosion and joint deformity. In some people, the condition can damage several body parts, including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart and blood vessels.
If you have rheumatoid arthritis, your immune system can cause inflammation inside one or several joints. It allows the body to send extra fluid and blood to a part of the body under attack from an infection. When the inflammation goes down, the capsule around the synovium remains stretched and can’t hold the joint in its proper position. It can cause the joints to become unstable and move into unusual positions.
It can affect anyone of any age and get worse quickly, so early diagnosis and intensive treatment are critical. However, new medications and advanced treatment methods have improved treatment options dramatically, preventing physical disabilities from severe rheumatoid arthritis.
Symptoms:
Rheumatoid arthritis can affect any joint in the body, although it is often felt in the small joints in the hands and feet first. As the disease progresses, several symptoms start occurring in the wrists, knees, ankles, elbows, hips and shoulders. In most cases, symptoms occur in the same joints on both sides of your body, such as:
- Tender, warm, swollen joints
- Joint stiffness usually gets worse in the mornings and after inactivity
- Fatigue, fever and loss of appetite
Over time, rheumatoid arthritis can cause joints to deform and shift out of place. However, its signs and symptoms may vary in severity and may even come and go. Nearly 40% of people who have rheumatoid arthritis also experience signs and symptoms that don't involve the joints. Areas that may be affected include:
- Skin
- Eyes
- Lungs
- Heart
- Kidneys
- Salivary glands
- Nerve tissue
- Bone marrow
- Blood vessels
If you experience any of these symptoms or have persistent discomfort and swelling in your joints for more than a week, make an appointment with your doctor to ensure timely intervention.
Causes & Risk factors
While exact causes of inflammatory arthritis are still unknown, doctors suspect a genetic component behind it. Your genes can make you more likely to react to environmental factors — such as infection with certain viruses and bacteria — that may trigger the disease. Common risks of rheumatoid arthritis include:
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop rheumatoid arthritis.
- Ageing: It can occur at any age, but it most commonly begins in middle age.
- Family history: If your close family member has rheumatoid arthritis, you may also have an increased risk of the disease.
- Smoking: Smoking increases your risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis, especially if you have a genetic predisposition for developing the disease.
- Obesity: People who are overweight are at higher risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis.
Diagnosis
Rheumatoid arthritis is harder to detect in its early stages because the early signs and symptoms are similar to many other diseases. Your doctor will start with a physical exam to check your joints for swelling, redness and warmth. They may also check your reflexes and muscle strength. If they suspect RA, they may also order additional tests, such as:
- Blood tests to check elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate or C-reactive protein level. Other common blood tests look for rheumatoid factor and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies.
- Imaging tests to help track the progression of rheumatoid arthritis in your joints over time. MRI and ultrasound tests can help your doctor judge the severity of the disease in your body.
Treatment
There are three types of treatments available for rheumatoid arthritis. However, the types of treatment recommended by your doctor will depend on the severity of your symptoms and how long you've had rheumatoid arthritis.
Medications: Common types of medications for RA include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, steroids, and conventional DMARDs to slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and save the joints and other tissues from permanent damage.. However, the types of medications recommended by your doctor will depend on the severity of your symptoms and how long you've had rheumatoid arthritis.
Physical therapy: A physical or occupational therapist can also teach you exercises to help keep your joints flexible and suggest new ways to do daily tasks that will be easier on your joints.
Surgery: If medications fail to prevent or slow joint damage, you and your doctor may recommend surgery to repair damaged joints, reduce pain and improve function. It may involve one or more of the following procedures:
- Synovectomy to remove the inflamed lining of the joint. It reduces pain and improves the joint's flexibility.
- Tendon repair to repair the tendons around your loose or ruptured joint.
- Joint fusion to stabilize or realign a joint and relieve pain if a joint replacement isn't an option.
- Total joint replacement to remove the damaged parts of your joint and inserts a prosthesis made of metal and plastic.
Why Eternal Hospital?
At Eternal Hospital, we have a highly qualified and dedicated team of urologists who are always committed to providing the latest and most advanced medical care to all our patients. Being a trusted name in healthcare, we act compassionately while ensuring confidentiality to those who need it. We have set high standards in patient-centric premium care and outstanding patient safety, and exceptional maintenance in a timely manner. In addition, we adhere to the use of up-to-the-minute innovations to offer state-of-the-art treatments to our patients with unparalleled results.