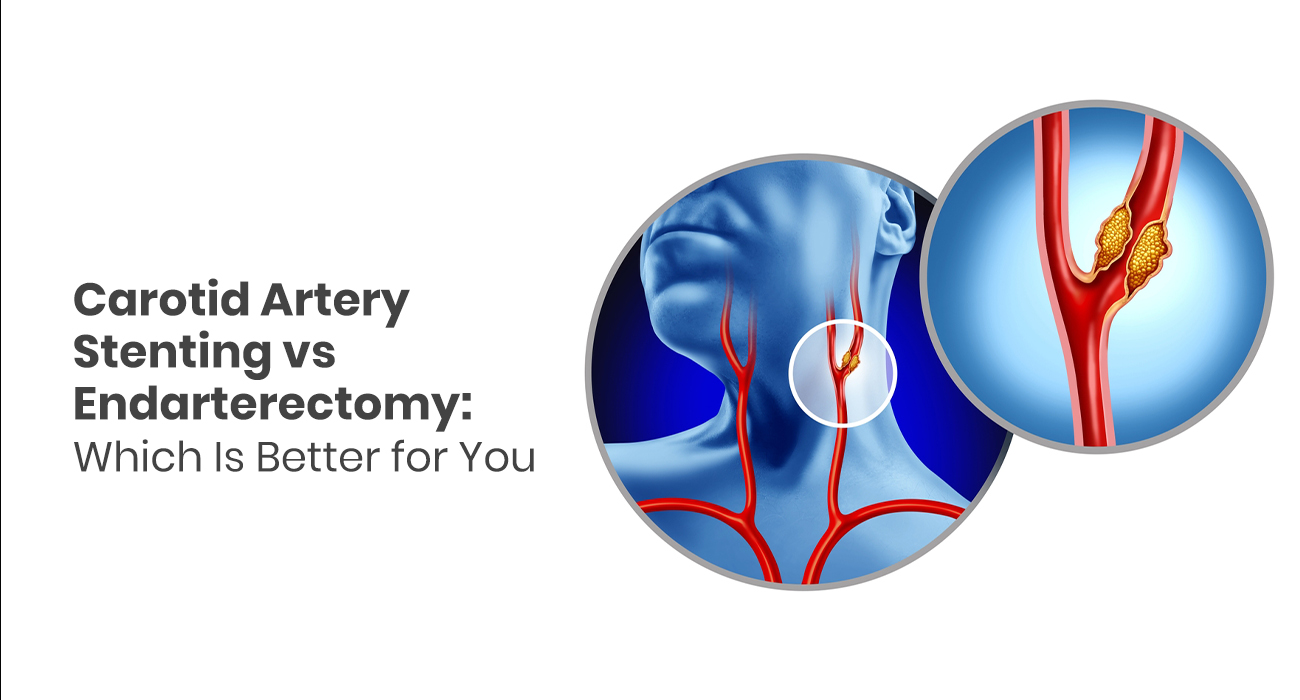
Carotid Stenting: A Life-Saving Procedure to Prevent Stroke
10/27/2025
You might face many instances in life where planning ahead could make all the difference. For example, if you want to crack a competitive exam, you analyze the past papers, concentrate most on the important topics, and then study hard to get the best outcome.
The same idea can be applied to your health. Due to many factors, you might notice early warning symptoms such as weakness on one side of the body, trouble speaking, etc. With these constant signs, you visit your doctor, and they may recommend tests like a carotid ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI. If these tests show blockage in the important carotid artery, the blood vessel that supplies the brain.
Your doctor can suggest timely carotid artery stenting, which can be a life-saving step. This procedure can ensure the best health outcome by restoring proper blood flow to the brain, reducing the risk of a stroke. Explore more about carotid stenting by reading the article.
 What is Carotid Stenting?
What is Carotid Stenting?
Carotid artery stenting is a medical intervention to prevent serious conditions like a stroke. After the healthcare professional performs a diagnostic procedure like a carotid ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, if these reflect any blockage in the carotid artery due to a buildup of fatty material (plaque). Doctors can recommend carotid stenting for an adequate blood supply to the brain, face, and neck.
What is a Carotid Artery?
The carotid arteries are the blood vessels situated on each side of your neck. These arteries are the primary arteries delivering oxygen-rich blood to your brain. Due to many lifestyle or health factors, they can be blocked with plaque (or unhealthy fatty deposits). This blockage can slow or stop blood flow to your brain (a medical condition known as carotid artery disease). If untreated, this condition can lead to a stroke.
Symptoms like one-sided weakness or other conditions/stroke, or ministroke symptoms
↓
Doctors perform diagnostic procedures (carotid ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI)
↓
If blockage in the carotid artery
↓
Doctors recommend carotid stenting
↓
Prevention of Stroke
 What Does Carotid Stenting Generally Treat?
What Does Carotid Stenting Generally Treat?
A carotid artery stenting procedure treats conditions known as carotid artery stenosis (narrowing)
Who Needs Carotid Stenting?
Doctors recommend this procedure to people:
- Who have stroke or ministroke symptoms from a carotid artery blockage (greater than 50%)
- A carotid artery blockage of 70% or more with no symptoms
The Alternative Names of Carotid Stenting
Carotid stenting is also known as:
- Carotid angioplasty and stenting
- Carotid artery stent implantation
- Carotid artery stenosis—angioplasty
Carotid Stenting—The General Procedure
A doctor follows the following steps to ensure you get the maximum benefits from carotid stenting.
A. Before Carotid Stenting
- The doctor will evaluate your past medical conditions, ongoing medicine, and allergies to blood thinners, dyes, or metals.
- You’ll be instructed not to eat or drink a day before (usually at night) in order to keep an empty stomach.
- On arrival, the medical staff will place sticky electrode pads on your chest to monitor your heart. They will evaluate the area where the stent is to be inserted
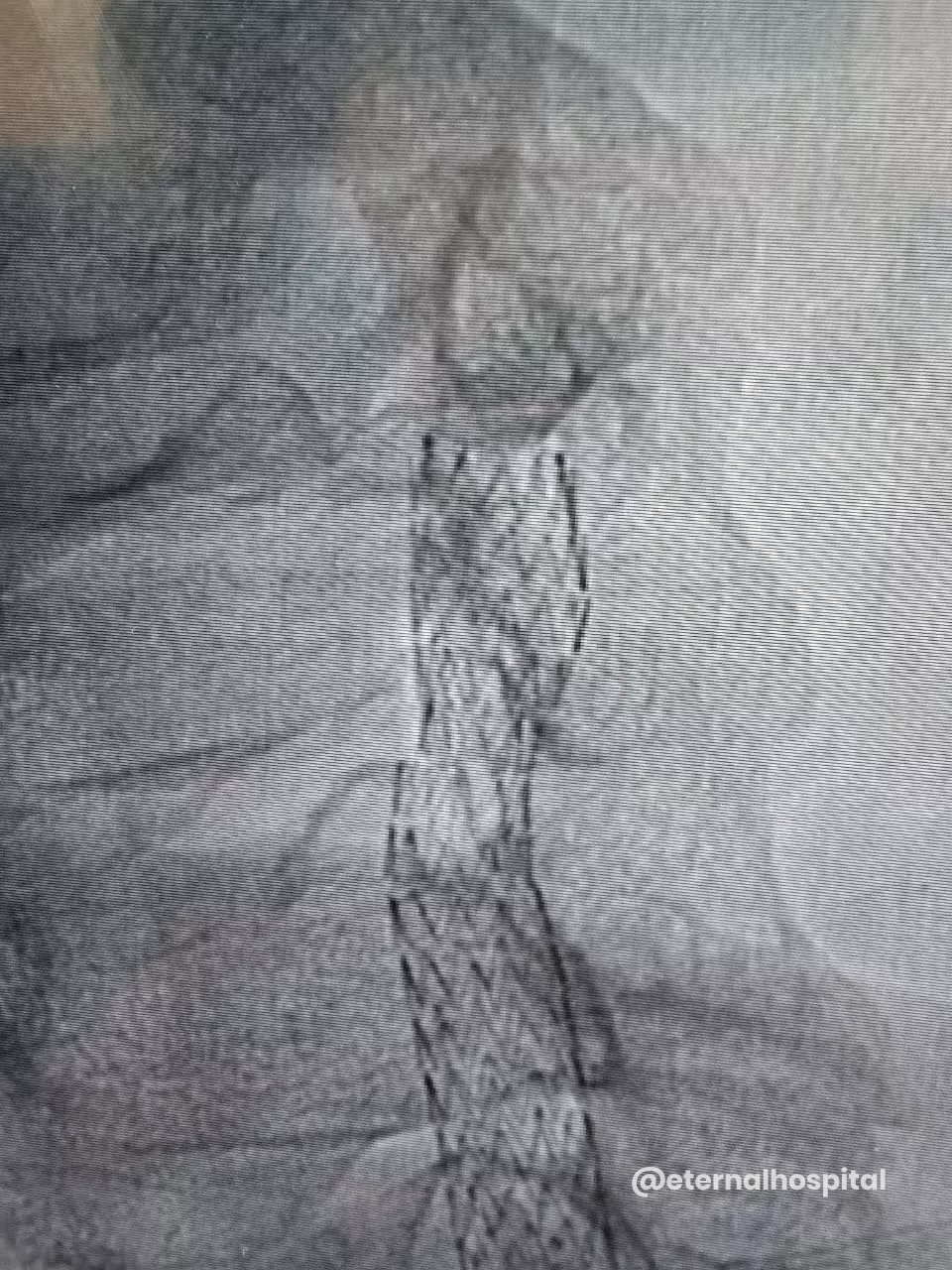
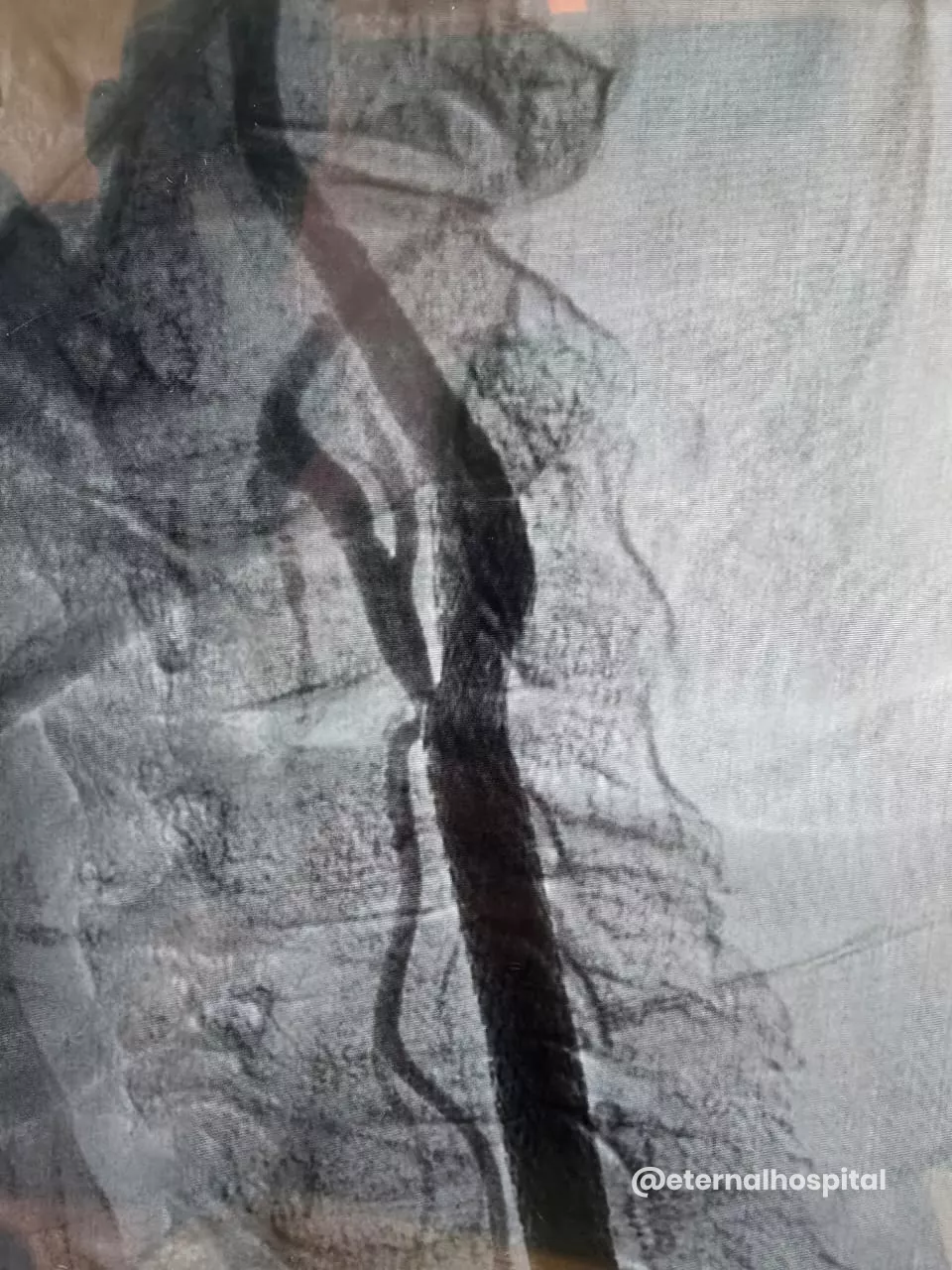
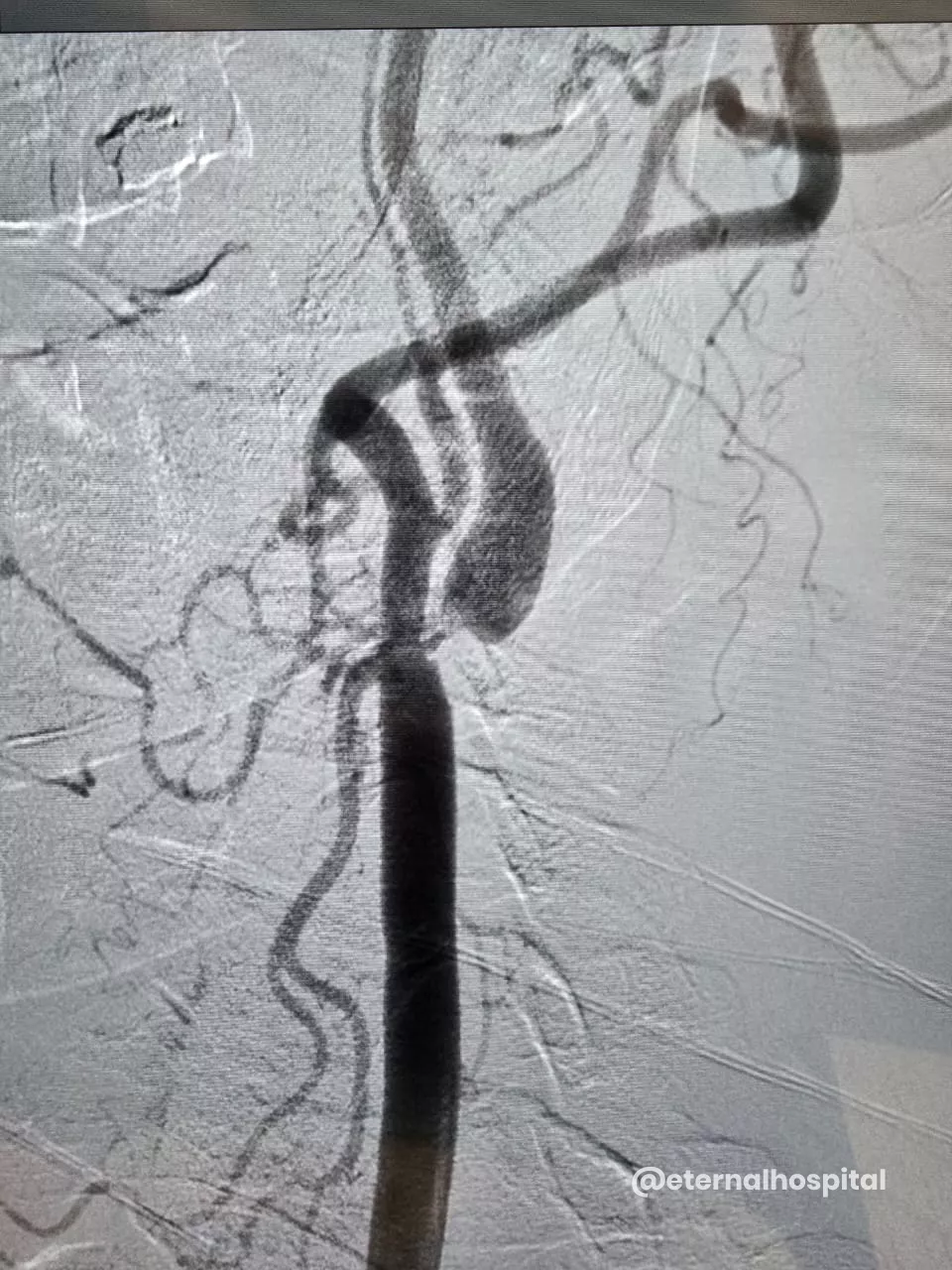 B. During Carotid Stenting
B. During Carotid Stenting
- The doctor numbs the insertion area, makes a small cut to the designated area, and inserts a thin tube (known as a catheter) into the artery.
- With the help of X-ray images, the thin tube is moved up to the narrowed section of the carotid artery.
- A tiny filter could be used to catch any loose debris.
- A small inflated balloon is used to expand the artery, and then the stent is fitted to keep the artery open.
- Afterward, the balloon and filter are taken out.
C. After Carotid Stenting
- You may be instructed to lie still for a few hours to prevent bleeding where the tube was inserted.
- The medical care team will monitor you for several hours (usually overnight observation).
- You’ll be given instructions to continue taking blood thinners. Take them as per the prescription.
- You will be required to follow lifestyle changes such as not smoking, managing blood pressure, and eating a healthy diet to help avoid further artery narrowing.
How Successful is Carotid Stenting?
Most individuals have experienced improved blood flow to their brains and have decreased their risk of a stroke after carotid artery stents. This treatment has a likelihood of being a lifetime repair in more than 95% of cases.
Benefits of Carotid Artery Stenting
It reduces the risk of stroke in most cases and offers the following benefits:
- Less invasive method
- Require smaller incisions or no incision
- Lower chances of nerve damage in the neck
- People experience less pain after the procedure
Risks/Complications of Carotid Artery Stenting
If done under a trustworthy professional, like in Eternal Hospital, the procedure is safe and effective. However, like other medical procedures, it can also carry risks, such as
- Bleeding at the catheter insertion site
- Stroke or ministroke (transient ischemic attack, or TIA)
- Blood clots
- Bleeding at the site in the groin or wrist where catheters were inserted
- Low blood pressure
- High blood pressure
- Slower than normal heart rate
Conclusion
Not taking early action, like carotid artery stenting for blockage, can increase the risk of stroke and long-term complications. Timely carotid stenting widens the artery and increases brain blood flow to help you live a healthy life. Adhering to your doctor’s advice and making healthy lifestyle changes is essential for the best possible outcome and lifelong health benefits.
Lifestyle changes that will help you maintain good results after carotid stenting are:
- Don't drink and smoke.
- Reduce bad cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Control other conditions, like diabetes and high blood pressure.
- Engage in regular prescribed exercise.
FAQs
Q1: Is a carotid stent a major surgery?
A: No, it is not considered major open surgery. Carotid stenting is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a tiny tube and X-ray guidance. This means smaller cuts/incisions are required, and faster recovery can be achieved.
Q2: How long is the procedure for a carotid stent?
It generally takes about 1 to 2 hours. However, the carotid stenting procedure depends on the individual's medical condition and anatomy.
Q3; How long is the life expectancy of a carotid stent?
Carotid stents often last for many years, with most individuals enjoying a long-term benefit. People have observed a reduced risk of stroke after this procedure.
Q4: Who are not the good candidates for carotid stenting?
People with the following conditions are not good candidates for carotid stenting:
- Certain vessel shapes, such as very twisted or heavily calcified arteries
- Recent stroke
- Ongoing bleeding issues
- Severe allergy to the stent material or dye
- Blocked arteries, or those who cannot take blood thinners
- Some heart problems or brain conditions
The healthcare professional will decide if carotid stenting is good for you or not.