What Is Osteoporosis? Understanding Bone Health and Risk Factors
10/17/2025
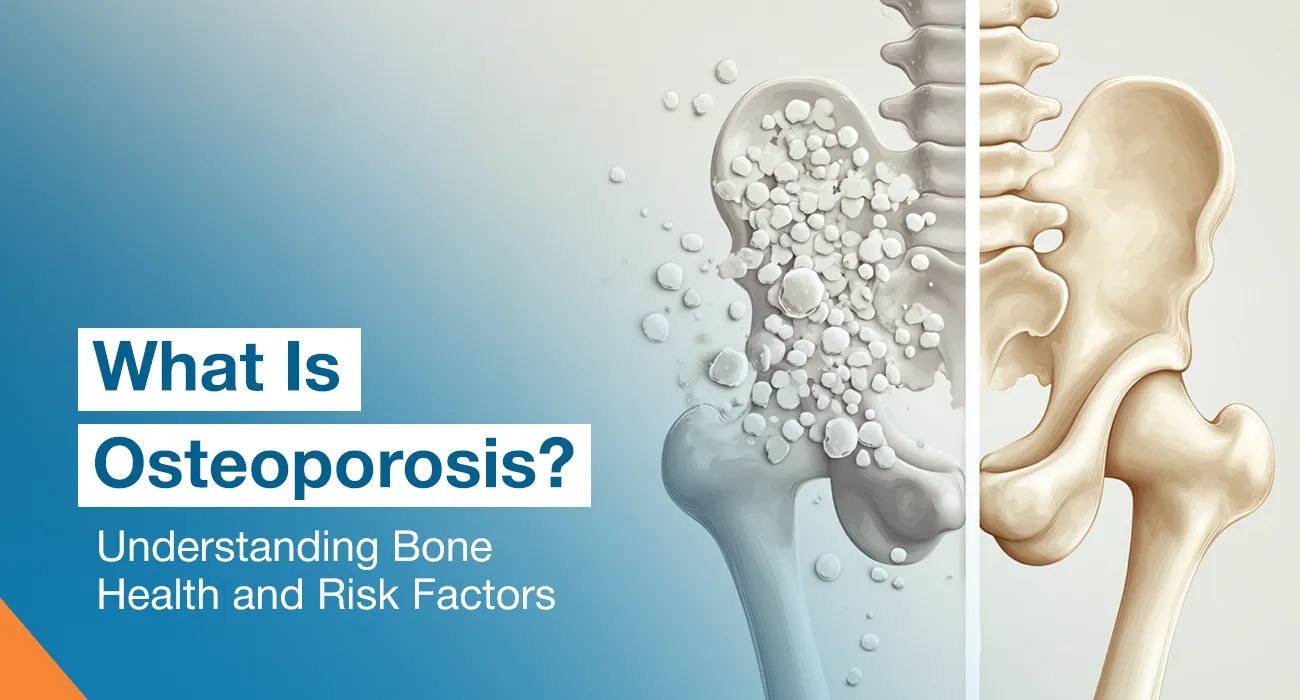
What Is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a bone disease. In this, bones lose their density and strength, becoming weak and fragile. It occurs when the body breaks down old bone more quickly than it can make new bone, resulting in porous, less dense bones.
Because of osteoporosis, even a small fall or minor stress can lead to fractures, particularly in the hip, spine, or wrist. It often develops gradually without symptoms until a bone breaks. It mainly affects older adults and postmenopausal women.
What's Really Happening in Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis happens when bone remodeling becomes imbalanced. It means old bone is broken down by cells called osteoclasts, and new bone is formed by osteoblasts, getting imbalanced. This leads to bones that are porous, weaker, and vulnerable to fractures. This imbalance is triggered by hormones, aging, and reduced bone formation activity.
What are the Risk Factors for Osteoporosis?
Here are some osteoporosis risk factors:
1. Lower Reproductive Hormones
Low levels of reproductive hormones like estrogen in menopause or testosterone in men can disrupt the balance between bone breakdown and formation. This leads to faster bone loss and fragile bones.
2. Anorexia Nervosa
This is a type of eating disorder. Due to irrational fear of weight gain, the person restricts nutrient intake relative to requirements. This leads to nutritional deficiencies and hormonal changes, lowering bone formation.
3. Low Calcium & Vitamin D Consumption
A diet low in calcium and vitamin D reduces bone mineralization (the process of deposition of minerals on the bone matrix). This impairs new bone formation, making bones porous.
4. Long-Term Medication
Long-term use of medicines like glucocorticoids and anticonvulsants increases bone tissue breakage and decreases bone formation. This promotes faster bone loss.
5. Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of weight-bearing exercise decreases the stimulation of osteoblasts (cells that create new bones and grow and heal existing bones). This leads to decreased bone density and strength.
6. Smoking
Chemicals present in smoke interfere with osteoblast function and calcium absorption. This leads to weakening of the bone structure.
7. Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol impairs calcium balance and blocks bone-forming cells. This increases the faster breakdown of bone.
8. Prolonged Bed Rest
Prolonged inactivity leads to rapid bone loss by reducing the mechanical force needed for healthy remodeling.
What are the Osteoporosis Symptoms?
According to the International Osteoporosis Foundation, osteoporosis affects 21.2% of women over age 50 and 6.3% of men over the same age globally.
It develops quietly; hence, early detectable signs of bone loss are rare. However, some of them are:
- Receding gums
- Weaker grip strength
- Weak and brittle fingernails
Once osteoporosis deteriorates further, you can experience more noticeable symptoms:
- Loss of height
- Fracture from a fall
- Back or neck pain
- Stooped posture (kyphosis) or fracture
- Shortness of breath (if disks in your spine are compressed)
Osteoporosis Prevention: Bone Health Tips
Here are the 10 simple ways to prevent osteoporosis:
1. Eat Food Rich in Calcium
Calcium is the fundamental ingredient for building and maintaining strong bones.
2. Get Sufficient Vitamin D
Vitamin D supports your body in absorbing calcium effectively to make bones stronger.
3. Do Weight-Bearing Exercise
Activities like walking and dancing stimulate bone growth and improve density.
4. Strength Training
Resistance exercises like push-ups, squats, and planks build muscle and support bone strength.
5. Avoid Smoking
Smoking damages bone density and impairs bone healing. Hence, avoid smoking to reduce your bone loss.
6. Avoid Alcohol Intake
Excessive drinking disrupts calcium absorption, leading to lower bone formation.
7. Get Morning Sunlight
Sunlight stimulates vitamin D production, which is important for calcium absorption.
8. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being underweight can increase bone loss; a healthy BMI supports better bone density.
9. Limit Caffeine Consumption
Enjoy caffeine in moderation, as excess can reduce calcium absorption, weakening bones.
10. Avoid Prolonged Inactivity
Keep yourself active to prevent bone loss by stimulating remodeling and maintaining density.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a doctor as soon as possible if you experience the following symptoms of osteoporosis:
- Excruciating pain.
- Unable to move a part of your body.
- A part of your body is distinctly different-looking.
- Your bone is visible through your skin.
- Swelling.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis can bring challenges in life that can be painful to manage, but with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment under professional care at Eternal Hospital, you can protect your bones and lead a healthy life. Take prompt action today to prevent fractures and improve quality of life.